10 Facts You Must Know About the Ethereum Merger
2022年08月08日
Mergers are confusing, so let’s start from the ground up and explain one of the most important events in the history of cryptocurrencies.
1. What is "the Merge"?
"Merge" is the name of the event for the Ethereum blockchain to transition from using a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.
It's called a "merge" because it's a merger of two separate blockchains currently running in parallel. The Ethereum mainnet is in the process of “merging” with a special-purpose blockchain called the Beacon Chain.
The Beacon Chain was launched on December 1, 2020 with the sole purpose of “becoming a proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain.”
There are no transactions on the Beacon Chain, and no Token or DeFi applications. It is an "empty chain" just to be a blockchain running the PoS consensus mechanism.
Because the beacon chain is an "empty chain", it can be merged with the Ethereum blockchain and replace Ethereum's PoW consensus mechanism without worrying about any other variables.
Once the two chains are merged, Ethereum's PoW verification will be replaced by a brand new PoS consensus mechanism.
2. Why is "merger" so popular?
The merger is considered one of the most important events in the history of cryptocurrencies since the birth of Bitcoin's "genesis block." There are many reasons for this.
First, in the history of cryptocurrencies, no blockchain has undergone such a major change.
It is very rare to change the operation mechanism of the blockchain, let alone Ethereum, no other blockchain has made such a major change after it has established a huge on-chain economy.
The market cap of ETH assets today is $203 billion (previously $550 billion), and the value based on its network is in the hundreds of millions. Ethereum has by far the strongest and most active economic ecosystem in cryptocurrencies, and the security of all these economic activities will move from PoW-based to PoS-based.
So if something goes wrong, the risk is huge. This is one of the main reasons why the merger took so long, with so much testing and refinement involved.
3. How will the merger affect ETH?
The merger will have a huge impact on the ETH economy, especially for investors.
The merger dramatically changed the ETH economy in two ways: reducing ETH issuance and using ETH as a native yield asset.
Reduce the amount of ETH issued
The merger will reduce ETH annual inflation from 4.3% to 0.43%.
This is because the PoS consensus mechanism will fundamentally improve efficiency. PoS aims to provide the highest level of blockchain security at the lowest cost. These cost savings will benefit ETH by reducing the amount of ETH issued to maintain security.
PoW is very expensive and requires a lot of resource overhead to reward miners for their services.
By contrast, the cost of securing PoS is simply the opportunity cost of capital and does not represent any real-world commodity or tangible cost. Unlike PoW, PoS does not need to issue a large number of tokens to pay for security fees. Therefore, these lower security costs make the PoS consensus mechanism more efficient.
Ethereum was able to reduce its annual ETH issuance from 4.3% to 0.43% due to the reduced need to pay PoW miners. A reduction in the issuance of new ETH is generally considered bullish.
This is because PoW miners immediately sell most of the rewards they receive, and over time the portion that gets sold makes up close to 90+% of the total mined.
With PoS, ETH will reduce production by more than 90%, and the overhead cost of being a PoS verifier will basically be reduced to 0.
Proponents of PoW believe that the high cost of maintaining PoW blockchains is only a feature of the PoW consensus mechanism, not a defect. They argue that these costs prevent centralization by creating churning in asset holdings, as this forces sellers to pay PoW miners. While PoW may indeed guarantee asset decentralization, it also creates security centralization.
4. Why is the combined ETH deflationary?
Almost exactly a year ago, on August 5, 2021, Ethereum introduced EIP-1559, an upgrade that changed the way Ethereum manages transaction fees. Rather than simply paying the full transaction fee to the miners, most of it is burned.
There are many reasons for this.
After the merger, the production of ETH will be reduced by at least 90%, and the proportion of ETH destroyed in each block will also increase accordingly.
When the gas cost of Ethereum is greater than or equal to 7gwei, the rate of ETH being destroyed will be greater than the rate of ETH issuance, reducing the total supply of ETH.
At the peak of the bull market, the gas fee price remained at 200gwei or higher for many months. Even in the current bear market, it can be reached.
Click here to review historical gas fees.
Click here to simulate the combined issuance of ETH.
5. Will the "merger" reduce Ethereum's gas fees?
Won't.
This is a misunderstanding caused by confusing the concepts of "Ethereum 2.0" (ETH 2.0) and "merger".
ETH 2.0 is the name of the future state of Ethereum that is no longer used by the Ethereum community. ETH 2.0 refers to a future version of Ethereum that will enable PoS and sharding.
There was a time in Ethereum’s history when it was believed that these two updates would happen at the same time, PoS and sharding. As R&D progressed, the developers realized they could separate these updates.
However, the moniker "ETH 2.0" has always existed.
Sharding will reduce Ethereum gas fees on L1, but for end users, the realization of really low gas fees or even zero gas fees will eventually happen on L2, such as Optimism, Arbitrum, Polygon, StarkNet, zkSync or others L2.
When Ethereum L1 gas fees are reduced, L2 gas fees will be reduced by an order of magnitude larger. The solution to Ethereum gas fees was never to lower fees on L1, but to move users to L2, where they can enjoy a performance-efficient, low-cost transaction experience.
6. Will the merger increase the transaction speed of Ethereum?
This is actually similar to the previous question, just expressed differently.
The transaction volume and transaction costs in the encrypted network will affect its supply and demand changes.
Ethereum’s block time (how often blocks are added to the Ethereum network) did get slightly faster after the merger, going from an average block time of 13.6 seconds to 12 seconds.
This means a 12% increase in transaction capacity and a 12% reduction in gas cost.
But this is an insignificant amount and should not be considered a "gas fee reduction".
7. Will the merger reduce Ethereum’s energy consumption?
Yes. will be greatly reduced. This is one of the main results of The Merge and PoS.
After the merger, the energy consumption of Ethereum will be reduced by about 99.95% compared to the current level.
PoS secures the blockchain with capital, not energy. So the energy required to keep Ethereum running after the merger is comparable to basic computer usage: like what you're doing right now, such as reading this article, sending a tweet, downloading a movie to your hard drive, etc.
With PoS enabled, the energy cost of Ethereum is just running a node — about 2.6 MWh per year. That's about 1,300 times less than the entire U.S. gaming industry consumes.
Ethereum will actually be the greenest financial system in the world.
Banking and finance still need people to drive around in gas cars and turn on lights in buildings, which is no longer needed in a crypto-powered world.
Maybe Wall Street should go green by using Ethereum ;).
8. Will Ethereum stakers sell their ETH after the merger?
No, they won't.
The ETH in the pledge cannot be withdrawn immediately after the Ethereum merger. This is to keep things as simple as possible, after all this is the biggest and most complex upgrade Ethereum has ever experienced in the industry.
The ETH in the withdrawal pledge is expected to be unlocked within 6-12 months of the merger.
So will stakers sell ETH immediately after unlocking?
Maybe, but there are still limitations. There is a withdrawal/deposit queue that limits how fast people can stake and unstake. This is again a mechanism to keep the chain stable, and will not let the rapid fluctuations of the Ethereum application layer affect the security of the chain.
The deposit/withdrawal bottleneck is limited to X/ETH per day, where X is equal to:
Number of validators / 65536, rounded down to the nearest integer.
The number 65536 is 2 raised to the 16th power. For some reason, Ethereum developers love these square numbers. It's called the Churn Limit Quotient, and you can read about it here and here.
Currently, there are 433,916 Ethereum validators on the Beacon Chain. To find how many validators per epoch, divide it by 65,536 and round down to the nearest integer.
433,916 (total validators) / 65,536 6 validators per epoch
So the activation/deactivation count is 6 validators per epoch. An Ethereum epoch is 6.4 minutes, 225 epochs in 24 hours.
Therefore, the current rate of validator activation/deactivation is 1,350 per day.
225 epoch*6=1350 epochs/day
Each validator has 32 ETH, so a maximum of 43,200 ETH is unlocked per day (32*1350).
Also, APY as an ETH staker increases after the merger, as ETH stakes also charge transaction fees.
This is expected to increase the ETH yield from 4.2% to 5%+, and even higher when gas consumption is high.
9. Why 32ETH?
Why does it take 32 ETH to run a node and not 31, 33 or any other number? The answer is that the more nodes, the more total message passing between nodes. If a node needs less ETH, more nodes can come online. While this is good for decentralization, it limits Ethereum scalability.
Choosing 32ETH is a compromise, which also comes from a square number, 2 to the 5th power.
Since node messaging is exponential, reducing the validator requirement from 32 ETH to 16 ETH would increase the amount of messaging for all nodes by a factor of 4. 32 was chosen as the minimum amount of ETH to be staked, which can also yield "finality" in 768 seconds or "2 epochs".

Is 32ETH permanent?
uncertain! It can of course be modified to 16 or lower with improved consumer hardware, message compression and better signature aggregation.
10. PoS is not on-chain governance
A common question (mainly from the Bitcoin camp) is that PoS is equivalent to the "fiat system" we were originally trying to get rid of.
What they mean is that whoever controls the capital controls the power.
This is a frustratingly wrong position, and many of those who often support it may be spreading it maliciously to discredit any consensus mechanism other than Bitcoin.
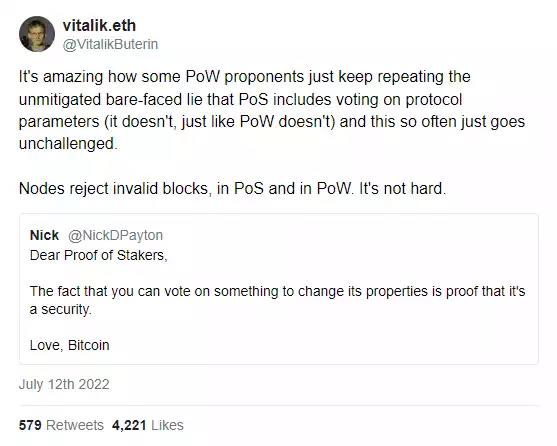
The role of an ETH validator is exactly the same as that of a PoW miner. This is a 1:1 comparison.
ETH holders do not have the governance rights of Ethereum. Like Bitcoin, this power is held by non-validating node operators, the "community".
Ironically, these camps advertise PoS as a scheme to “make the rich richer,” when the indisputable fact is that PoW mining facilities lead to higher returns on investment for wealthier capital.
TL;DR
PoS Ethereum with ETH native yield is the most democratized consensus mechanism as it offers the same proportional return as 32, 320, 3200 or 32,000 ETH.
They will all receive the same yield of around 5%.
This is in stark contrast to PoW miners, where a $100 million investment in a mining facility would generate well over 10 times more computing power than a $10 million investment due to the economies of scale that PoW hardware and energy costs can bring.
previous page
Recommended news
LianLi welcomes visitors to Booth TB09b at iTherM 2025. discover advanced liquid cooling solutions for AI, HPC, and next-generation data centers.
Looking for a crypto mining container for sale? Compare crypto mining containers, cooling types, capacity, and real deployment tips. Find the best crypto mining containers for sale for mining farms in 2025.















